Linux software package management
Contents
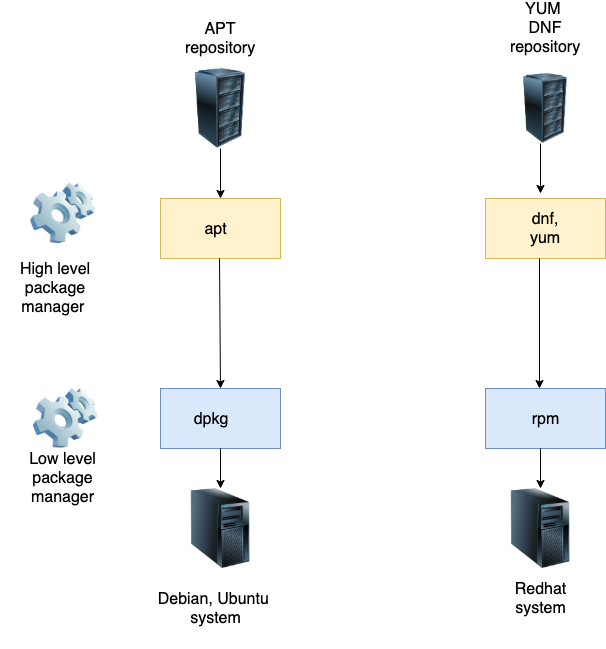
2. Linux software package management¶
2.1. Outline¶
Debian and Ubuntu packages.
Advanced Package Tool (APT) for package installation, removal, search, and query.
Debian package tool (dpkg) for package installation, removal, and query.
2.2. The purpose of Linux packages¶
All files in Linux distros come in packages. Packages are used for the following tasks:
Install software
Remove software
Update installed software
Fix broken or partly removed software files
Reconfigure installed software
2.4. Ubuntu (Debian) packages¶
Debian and Ubuntu OS components and most of the GNU software are available in form of packages. A package file contains:
Software
Info (control) file
Scripts (pre/post install/remove)
md5sum file hashes
Naming convention:
(package-name)_(source version)-(package-version)_(architecture).deb
For example:
make_4.3-4.1_amd64.deb
2.5. Installing Debian/Ubuntu packages with APT (Exercises)¶
Login to your LXC server.
Try executing command make, which doesn’t exist on the server yet:
make
The system error comes: The program ‘make’ is currently not installed.
You can install it by typing: sudo apt install make Install recommended package make by running apt install:
apt install make
You should be able to run command make now.
Simulate package installation by using option -s:
apt install -s netpbm
Notice the prerequisite library package that would get installed, libnetpbm10 Download the package without installation:
apt install -d netpbm
Notice the deb files with the packages in the apt cache directory:
ls -l /var/cache/apt/archives
Another way to download a package and get it in the current working directory:
apt download netpbm
Install the package:
apt install netpbm
Updating all the installed packages
apt update
apt upgrade
The APT repository and software folders are defined in file
/etc/apt/sources.list and optionally in directory /etc/apt/sources.list.d
2.6. Removing Ubuntu packages with APT (Exercises)¶
Remove package make by running apt remove:
apt remove make
Simulate package removal by using option -s:
apt remove -s netpbm
Notice package libnetpbm10 won’t be removed Simulate package removal with the dependencies:
apt autoremove -s netpbm
Notice the both packages would be removed. Remove the package with the dependencies:
apt autoremove netpbm
Both netpbm and libnetpbm10 should be gone now.
2.7. Search and quiry Ubuntu packages with APT (Exercises)¶
First, update the available package list from the Ubuntu repository:
apt update
If you are looking for a package with exact name, for example, make, use
apt list make
Search for packages containing string make in their name or description:
apt-cache search make
Narrow down the search results for the names containing make:
apt-cache search --names-only make
Filter the output for word make
apt-cache search --names-only make | grep -w ^make
Get the information about package make:
apt-cache show make
List the packages that depend on package make. Forcefully removing make would break these packages.
apt-cache showpkg make
Show the packages a given package depends on:
apt-cache depends make
2.8. Quiry Debian/Ubuntu packages with dpkg (Exercises)¶
What packages are installed on the system?
dpkg -l
Quiry package status with dpkg:
dpkg -s make
dpkg -s tzdata
List the files contained in the package:
dpkg -L tzdata
What package contains a file? For example, command /bin/ls
dpkg -S /bin/ls
Reconfigure a package with command dpkg-reconfigure after installation:
dpkg-reconfigure tzdata
To see the current package configuration, command debconf-show can be used, for example:
debconf-show tzdata
If there is no package dependencies, then a package can be installed with command dpkg. Otherwise, use APT. Install package make:
dpkg -i make_4.3-4.1_amd64.deb
To see the list of the files, contained in the deb package file:
dpkg --contents make_4.3-4.1_amd64.deb
Remove package make by using command dpkg:
dpkg --purge make