Warewulf 4 installation and configuration steps.
Contents
14. Warewulf 4 installation and configuration steps.¶
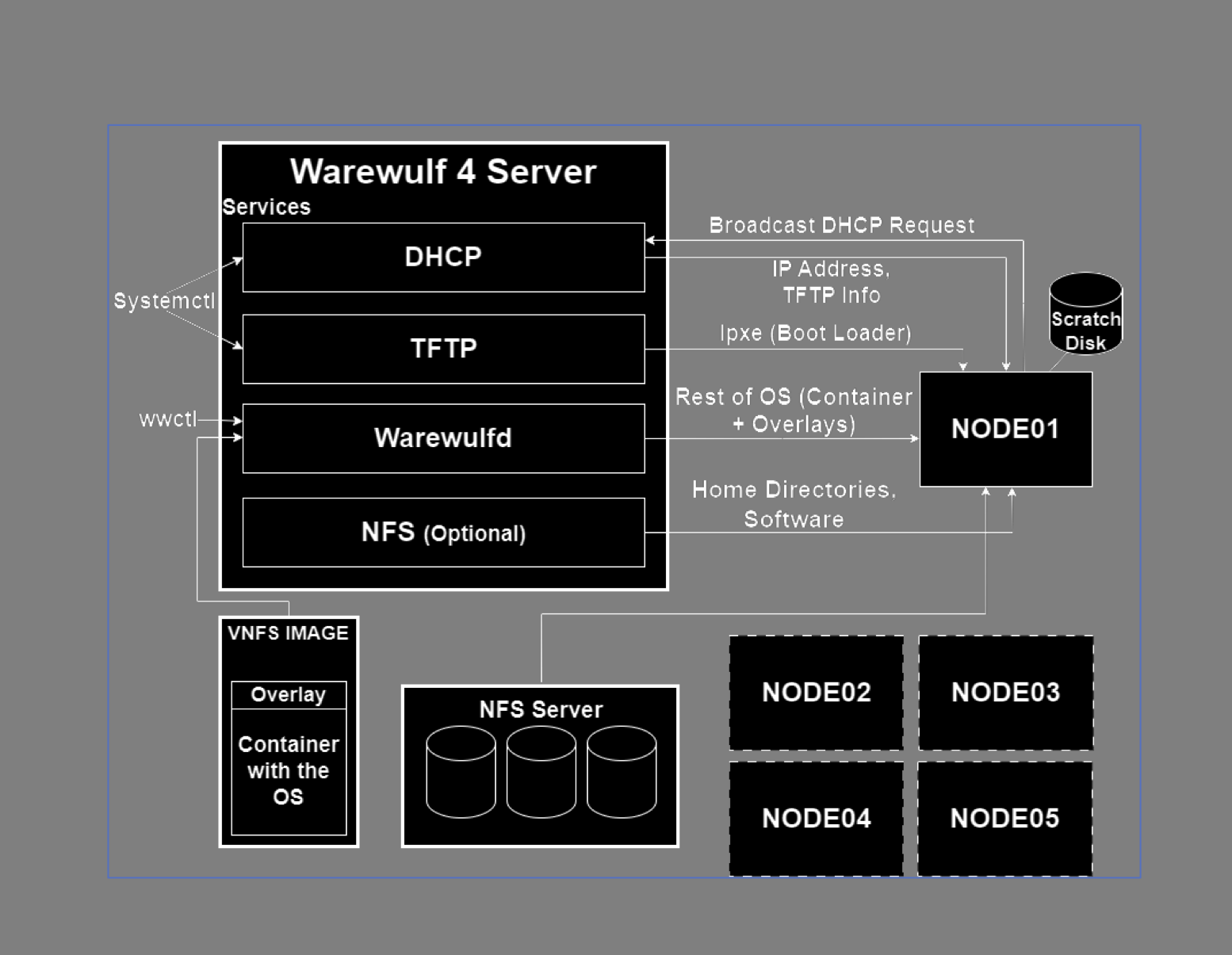
Warewulf project is meant for provisioning stateless operating systems with VNFS.
Previous versions of Warewulf were written in Perl, and build VNFS in chrooted environment.
Warewulf 4 is written in Golang and uses containers for building VNFS. Using chroot for building VNFS is also possible.
The installations below should be done in your new container, wwct0x, which has sufficient disk space for
the software we need to install.
We’ll compile warewulf from source, written Golang (GO) programming language.
14.1. Install prerequisite packages, including Golang version 1.20.¶
Golang 1.20 is available via apt from the packports repository.
Edit file /etc/apt/sources.list and add the line below in the bottom of the file:
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm-backports main contrib
Run command to update apt caches:
apt update
Install prerequisite packages:
apt install curl unzip make liblzma-dev
apt install tftp-server
apt install nfs-common
apt install nfs-kernel-server
apt install isc-dhcp-server
apt install git
apt install podman
apt install net-tools
Install Golang 1.20:
apt install golang-1.20 golang-1.20-go
14.2. Download warewulf source.¶
Fetch warewulf source from the git repository. Do the procedures below as user hostadm:
mkdir git
cd git
git clone https://github.com/hpcng/warewulf.git
cd warewulf
See available branches in the git repository:
git branch -r
Checkout 4.5.x branch:
git checkout origin/v4.5.x
14.3. Compile and install warewulf.¶
Set the PATH environment variable for the Golang compiler:
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/lib/go-1.20/bin
Compile the source:
make
Install the binaries in /usr/local:
sudo make install
Install the arm64 support in gcc compiler:
sudo apt install gcc-aarch64-linux-gnu
Build iPXE loader:
sudo bash scripts/build-ipxe.sh
Make the 3 iPXE files are in directory /usr/local/share/ipxe:
ls /usr/local/share/ipxe
We should see the following files:
bin-arm64-efi-snponly.efi bin-x86_64-efi-snponly.efi bin-x86_64-pcbios-undionly.kpxe
14.4. Settings for TFTP server.¶
Edit file /etc/default/tftpd-hpa to make the content as follows:
file content
TFTP_USERNAME="root"
TFTP_DIRECTORY="/var/lib/tftpboot"
TFTP_ADDRESS=":69"
TFTP_OPTIONS="--secure -vvv"
14.5. Configure DHCP server settings.¶
Edit file /etc/default/isc-dhcp-server to specify the network interface, eth0, for the DHCP traffic,
and disable ipv6:
content:
INTERFACESv4="eth0"
#INTERFACESv6=""
14.6. Configure warwwulf.¶
Edit file /usr/local/etc/warewulf/warewulf.conf and modify the entries for
ipaddr, netmask, network, range start, range end, dhcp systemd name, tftp systemd name.
For the ipaddr, put the IP address of your current container.
For the range start and range end, put the IP address of your node.
Anything else should look as below:
WW_INTERNAL: 45
ipaddr: 192.168.5.128
netmask: 255.255.255.0
network: 192.168.5.0
warewulf:
port: 9873
secure: false
update interval: 60
autobuild overlays: true
host overlay: true
syslog: false
datastore: /usr/local/share
grubboot: false
dhcp:
enabled: true
template: default
range start: 192.168.5.8
range end: 192.168.5.8
systemd name: isc-dhcp-server
tftp:
enabled: true
tftproot: /var/lib/tftpboot
systemd name: tftpd-hpa
ipxe:
"00:00": bin-x86_64-pcbios-undionly.kpxe
"00:07": bin-x86_64-efi-snponly.efi
"00:09": bin-x86_64-efi-snponly.efi
"00:0B": bin-arm64-efi-snponly.efi
nfs:
enabled: true
export paths:
- path: /home
export options: rw,sync
mount options: defaults
mount: true
- path: /opt
export options: ro,sync,no_root_squash
mount options: defaults
mount: false
systemd name: nfs-server
ssh:
key types:
- rsa
- dsa
- ecdsa
- ed25519
container mounts:
- source: /etc/resolv.conf
dest: /etc/resolv.conf
readonly: true
paths:
bindir: /usr/local/bin
sysconfdir: /usr/local/etc
localstatedir: /usr/local/var
ipxesource: /usr/local/share/ipxe
srvdir: /usr/local/srv
firewallddir: /usr/lib/firewalld/services
systemddir: /usr/lib/systemd/system
wwoverlaydir: /usr/local/var/warewulf/overlays
wwchrootdir: /usr/local/var/warewulf/chroots
wwprovisiondir: /usr/local/var/warewulf/provision
wwclientdir: /warewulf
Configure warewulf by running the command blow.
wwctl configure --all
Make sure it completes without errors. Otherwise troubleshoot the settings.
Enable and start service warewulfd:
systemctl enable --now warewulfd
See. if it is running:
wwctl server status
Command wwctl should run as root.
14.7. Modify DHCP server settings¶
Edit file /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf, and change the bottom of the file to disable
the dynamic range, and serve the IP address to your node. The example below is for node08.
Change the settings for your node.
# range 192.168.5.8 192.168.5.8;
dhcpd.conf bottom
host node08 {
hardware ethernet 0c:c4:7a:81:cc:b6;
fixed-address 192.168.5.8;
option host-name "node08";
}
The entries for the IP address and MAC address (hardware ethernet).
Find out the MAC address of your node:
ping -c 2 node08
arp -a
Take the MAC address and place it in file /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf for the hardware ethernet.
Restart the DHCP server:
systemctl restart isc-dhcp-server
14.8. Option 1: Pull and build the VNFS container.¶
wwctl container import docker://ghcr.io/warewulf/warewulf-debian:12.0 warewulf-debian:12.0
Edit the container with the command below. Option --bind /:/mnt provides the local file system on the server as /mnt to the container:
wwctl container shell --bind /:/mnt warewulf-debian:12.0
Install editor nano and command less in the container:
apt update
apt install nano less
Copy the warefulf.conf from the system to the container. It is inneded for service winit on the warewulf client.
mkdir /usr/local/etc/warewulf/
cp /mnt/usr/local/etc/warewulf/warewulf.conf /usr/local/etc/warewulf/
Reset the root password with command
passwd
Give the password we usually use for our LXC containers.
Exit from the container:
exit
14.9. Option 2: Build VNVF container in podman.¶
Now we are going to build a container on our system.
Download warewulf container configurations:
cd ~/git
git clone https://github.com/warewulf/warewulf-node-images.git
Let’s build podman container and name it debian_local:
sudo podman build -f git/warewulf-node-images/debian/Containerfile --tag debian_local
Check what containers podman can see:
sudo podman images
Export localhost/debian_local into tar file debian_local.tar:
sudo podman save localhost/debian_local -o debian_local.tar
Import the tar file into a warewulf container:
sudo wwctl container import file:///home/hostadm/debian_local.tar debian_local
Check what containers warewulf sees:
wwctl container list
Login to the container, install packages nano, sudo, and less:
sudo wwctl container shell --bind /:/mnt debian_local
apt install nano sudo less
Copy the warefulf.conf from the system to the container. It is inneded for service winit on the warewulf client.
mkdir /usr/local/etc/warewulf/
cp /mnt/usr/local/etc/warewulf/warewulf.conf /usr/local/etc/warewulf/
Reset the root password with command
passwd
Exit from the container:
exit
14.10. Set up the default node profile.¶
In this case, we assign container debian_local to the default profile.
wwctl profile set --yes --container debian_local "default"
wwctl profile set --yes --netdev eno1 "default"
Once those configurations have been set, you can view the changes by listing the profiles as follows:
wwctl profile list -a
14.11. Add a node¶
Adding nodes can be done while setting configurations in one command. Here we are setting the IP address of eno1 and setting this node to be discoverable, which will then automatically have the HW address added to the configuration as the node boots. Instead of node08, use your node name and its IP address.
wwctl node add node08 --ipaddr 192.168.5.8
wwctl node set node08 --discoverable true
To make node changes effective
wwctl overlay build
The node should be bootable from the network now.
14.12. Booting the node from the network¶
Navigate your browser to the BMC of your node, for example
https://bmc08. Use your node number please.Login as the admin user.
In the menu, select
Remote controland scroll down toiKVM/HTML5Click on
iKVM/HTML5. It will pop up the terminal for your node.Use the virtual keyboard to reboot the node by selecting
Ctrl-Alt-DelAt the BIOS bootup prompt, select
F12Wait until the system boots up into the warewulf image.
Login as root.
From your LXC container, try SSH to the node as user hostadm. You shouldn’t be able to because the network is not correctly configured on the node.
